2D Plotting
Plotting y=f(x) on the interval [-.1,.1]:
-
First create a vector of (e.g.) 200 equally spaces values between -.1 and
.1.
-
x1=linspace(-.1,.1,200);
-
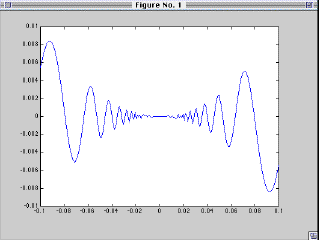
Suppose f(x) is an algebraic expression of standard functions such as f(x)=
x^2*sin(1/x).
-
Then the following computes the y values from the x values.
-
y1 = x1 .^ 2 .* sin(1 ./ x1);
-
Now put up the plot:
-
plot(x1,y1)
- Styles and colors mady be indicated e.g. by
- plot(x,y,'r--')
- where r indicates red, -- indicates dashed,
: indicates dotted, and * means starred.
- Titles, xlabels, ylabels, and text can be added by
- title('Graph Illustrating ...') ; xlabel(' ... ') ; text(x0,y0,'string')
etc.
- Axes can be drawn by
- axis([xmin xmax ymin ymax])
Adding Additional Graphs:
can be accomplished by:
-
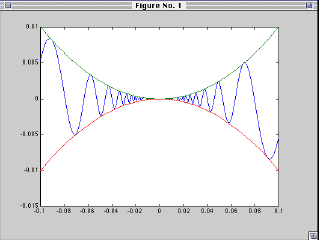
x2=linspace(-.1,.1,50);
-
(Note that this function oscillates less, so we take a coarser grid with
only 50 points.
-
y2 = x2 .^2
-
y3 = -x2 .^2
-
plot(x1,y1,x2,y2,x2,y3)
Another Way to Combine Pictures:
is to use the commands
- Hold on
- to cause additional pictures to be superimposed on the existing one
- Hold off
- to restore the default of replacing an old picture by a new one.
More sophisticated control of pictures is also possible via Matlab's handle graphics
facility.
Plotting a Function Defined in an m-file:
- Contents of m-file fcnname.m on the interval [a,b] is plotted by
- fplot('fcnname',[a,b])
Last Update: September 25, 2000
[Mathlab Home | Math]